You should probably eat more protein
"Too little" protein is definitely an issue, but is "too much" protein even a thing?
What’s wrong with the food in this picture?
This is one family from America’s weekly groceries per Time Magazine’s 2013 article Hungry Planet: What the World Eats. The family actually looks pretty trim and healthy, but if someone were to critique their groceries, they might say it’s too much processed carbs, others would say it’s too much sugar and salt, others would say it’s too much fat and some might say there’s too many animal products.
Next, consider this:
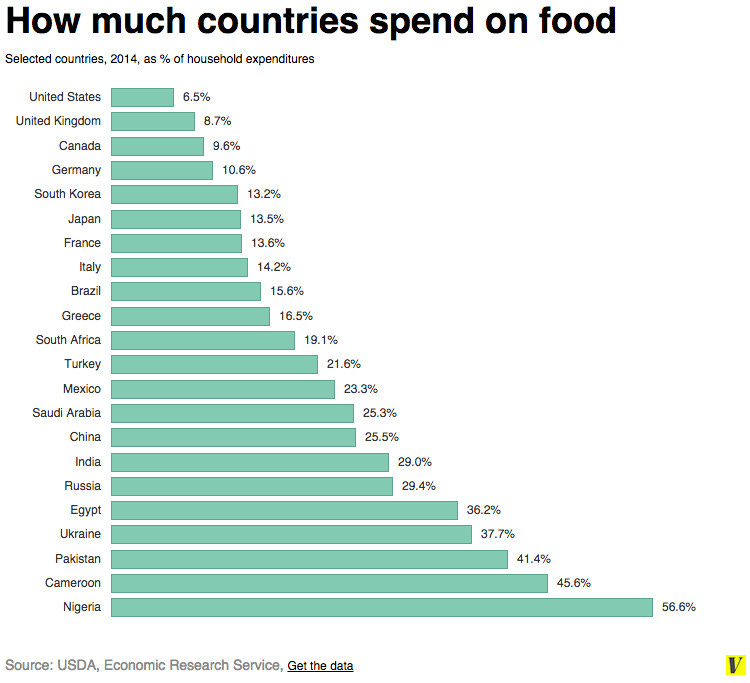
Reporting on USDA data, Vox claims that “Americans devote just 11 percent of their household spending to food, a smaller share than nearly every other country spends on food consumed at home alone.” Now part of this is because America is a wealthy nation so people don’t have to spend much on food, but considering America spends a lot less than France or Norway, part of it is likely due to the fact that Americans simply buy cheaper food.
I don’t think you’d be surprised to hear that cheaper food makes you fat. It’s true that cheap processed food is loaded with processed carbohydrates and seed oils, but what it doesn’t have much of is protein. Protein is the most expensive macronutrient.
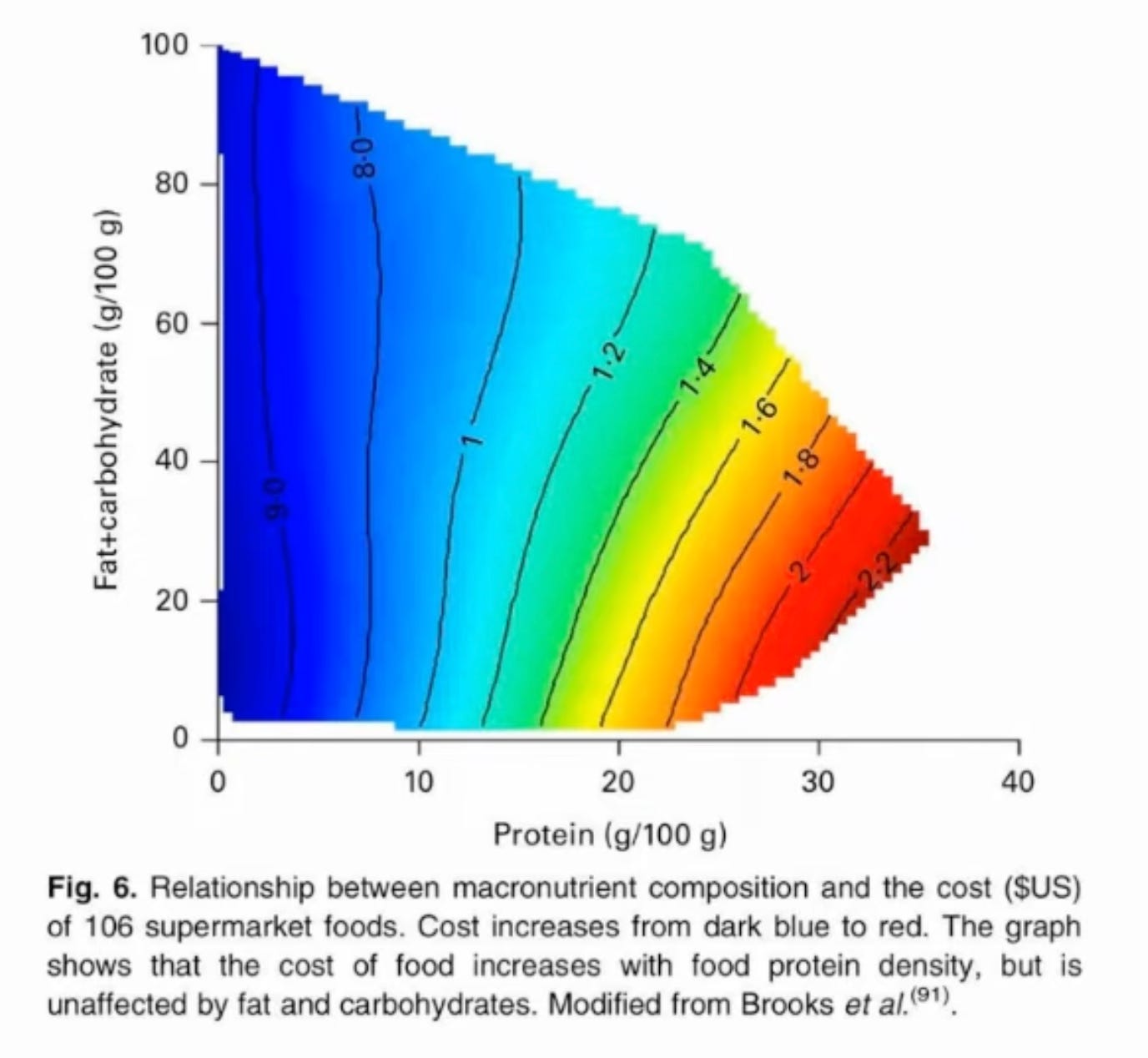
This study found that foods high in fat and/or carbohydrate were cheaper, and the more protein a food had, the more expensive it was.
NLSY79 data suggests that as income goes down, obesity goes up.
So of course cheap foods have all kinds of negative attributes, but could protein have anything to do with obesity?
Here’s the spoiler alert courtesy of Dr. Ted Naiman :
“Every single human obesity study you will ever look at, ever, at all, period, in the history of medical literature - the more protein people ate, the better. Always. Completely. Like, there's no exception."
Ted Naiman’s philosophy on maintaining a healthy weight is really simple. You need to improve your protein to energy ratio. Try and look at the macronutrients like this: We need protein to build our muscles, maintain our cellular machinery and so on: it builds us up and maintains our biological machinery. Fat and carbs we’ll consider as just an energy source. So you want to get plenty of grams of protein per calories of fat and carbs. Protein : energy. For example, a ribeye steak has plenty of protein and plenty of fat but no carbs, so its P:E ratio is 0.7. Lean beef has no carbs and even less fat, so its P:E ratio is 1.0 . Then of course things with tons of calories relative to protein are going to have really low P:E ratios - potatoes and peanuts have a P:E of 0.2 .
An interesting way to think about it is that the body of a lean, healthy person would have a pretty high protein to energy ratio. They would have plenty of skeletal muscle, not so much fat on their body. The more overweight and unhealthy you become, the lower your protein to energy ratio will become.
Keep reading with a 7-day free trial
Subscribe to Joseph Everett’s WIL Newsletter to keep reading this post and get 7 days of free access to the full post archives.