The $200 Billion Industry shrinking our brains
How a completely new food ingredient could be de-evolving our brains
Back in 1979, researchers were shocked to see a notable decrease in the average IQ of children in Massachussets. Not only were these kids slower at learning, but something was affecting their brain to where they more distractible, hyperactive, impulsive and easily frustrated. In the 1920’s Thomas Midgley had just made a new product for the automotive industry that he projected would make billions of dollars. The product essentially was an additive to gas that made car engines work better, but most importantly, it was very cheap compared to other alternatives so it could turn a big profit. Unfortunately it was a poison that would accumulate in the air and affected people’s brains. Just a year after Thomas Midgley showed symptoms of acute poisoning from his own product, he would state in a press conference that it was actually perfectly safe. That product was tetraethyl lead which was used to make leaded gasoline. From the 1920’s, cars all over the country were pumping the poisonous lead into the air every day. This dramatic change in the air lead to a decline in the IQ of children. Luckily, our brains are now safe from this because leaded gasoline was phased out starting in 1973.
So why has IQ stopped growing? IQ has been slowly and steadily increasing since the early 1900’s, but this effect seems to be slowing down and possibly reversing, according to Richard Haier.
In 2018, Norwegian researchers revealed data that IQ scores started to slightly decrease for men born after 1975. The lead author, Ole Rogeburg says that similar studies in Denmark, Britain, France, the Netherlands, Finland and Estonia all found the same thing - a trend of decreasing IQ scores. Now Rogeburg points out that someone might criticize this finding saying because IQ has a lot to do with genetics ‘maybe it’s just more dumb people are having more kids.’ But he says No, it has to be environmental factors because they found the same downward trend in IQ within families.
Dr. Michael Crawford, Director of the Institute of Brain Chemistry and Human Nutrition says that based on current trends that we are “heading for an idiocracy.”
There are tons of factors to IQ, but evidence is piling up that a different cheap and profitable invention is now polluting our brains. This completely new and unnatural product has created a $212 billion dollar industry …and it’s not in the air, but our food supply.
Dr. Michael Crawford’s data suggests that a specific type of fat added to the global food supply may be de-evolving our brains. That is a huge claim so let’s unpack what makes our brains so big and smart in the first place.
Lucy, the worst rated movie of Scarlett Johansson’s career, has a scene where her brain becomes so powerful that she can travel back in time, allowing her to meet a human ancestor, also named Lucy. You see, Lucy is one member of a species of primate that really existed 3.2 million years ago. Primates brains leading up to Lucy’s kind had been growing very slowly and steadily. However, something happened around 2 million years ago. Brain size started mysteriously increasing way faster, ending up with humans having massive brains way ahead of schedule. In fact, the human brain is so abnormally large that if height increased in size at the same rate that brain volume did, female humans height today would be over around 8.5 feet or 260 centimeters.
So why did this happen? And why are cetaceans like dolphins, orcas and whales so smart? And why are rhinos, cows and horses so dumb?
One theory is that early humans essentially figured out how to cook wild potatoes (tubers) which gave them plenty of calories to fuel their big, energy-hungry brains. The human brain takes up a whole 20-25% of our calories so an efficient source of calories was very important.
Except this doesn’t make that much sense because wild potatoes don’t have any of the important nutrients the brain needs to run - they’re just calories. Hunting would be a much better reason for why brains grew: Animal meat and organs would provide all sorts of critical nutrients for the brain and animal fat would provide tons of calories. Primates figuring out how to get meat was the most obvious explanation for evolving the human brain.
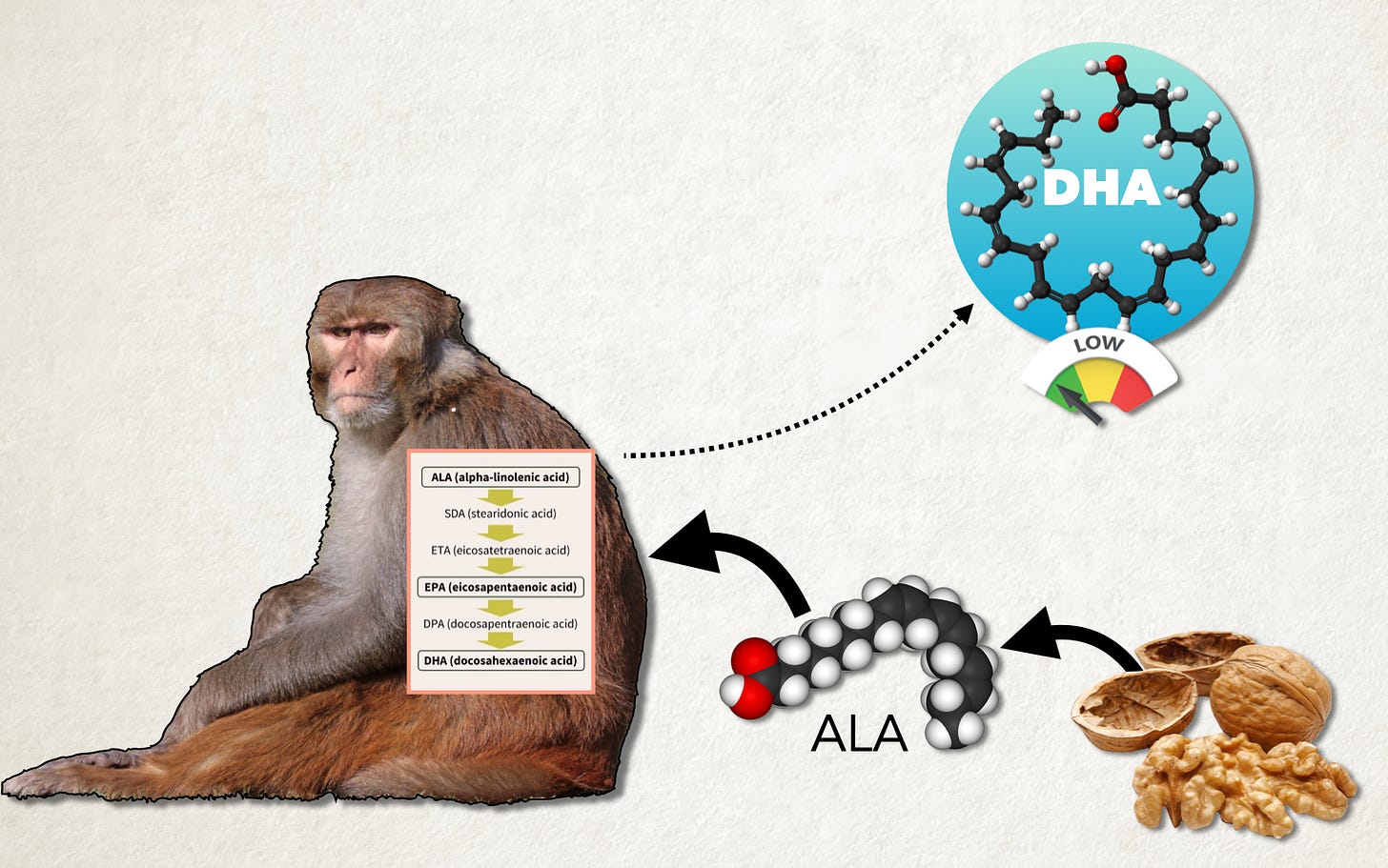
However, zoologist Dr. Michael Crawford thought there was another piece to the puzzle. In the 1980’s, he decided to investigate what specific types of fat were in the brains and body of various animals. He noted that high levels of two fats helped make the brain grow, but there was a third fat that seemed to be bad for brain growth. The two fats that made the brain grow and therefore were very important for the evolution of the brain are arachidonic acid (AA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA).
Humans could get plenty of AA by hunting various land animals, but land animals aren’t that great a source of DHA. You can get a good amount of DHA from the brains and eyes - but early humans would have had to crack open a lot of animal skulls to get a steady supply of DHA. Crawford argues that the real reason brains evolved was because early humans found a more simple way to get plenty of the special DHA.
Now primates like humans and monkeys have enzymes that can make a very small amount of DHA from a fat in plant foods. So, to get a lot of DHA you can’t make it, you have to eat it. The average monkey diet does not naturally contain much DHA …so what happens if you give monkeys DHA?
A 2014 paper outlines the work of some dedicated researchers at the University of California Davis who took some Rhesus monkeys and fed them a diet high in DHA for the entire lifespan of the monkeys - 17-19 years. After all this they put the monkeys in a brain scanner to see if anything was different. They found that compared to other monkeys, the brains of the monkeys on the unnaturally high DHA diet … had highly connected and well organized neural networks which in some ways “resembled the healthy human brain.” That is, some aspects of their brains started to look more like a human brain.
This information in the wrong hands could be dangerous. Monkeys are already smart enough to steal tourists’ stuff and hold it ransom for food…
The best source of DHA is seafood - fish, shellfish, crustaceans, algae. These have all kinds of important brain nutrients like protein, vitamin A, zinc, choline, iodine, selenium, vitamin B12 and so on but they would be the best source of DHA. Michael Crawford says it would be so easy and safe to just walk along the coastline and gather tons of nutrient dense food versus having to hunt land animals. Professor Stephen Cunnane of Toronto University agrees, saying ‘A shore-based diet was essential for the evolution of human brains.'
One study from 2020, found that breastfeeding mothers who ate more omega-3 fats like DHA tended to have babies with bigger brains. Specifically, the frontal cortex got bigger - the frontal cortex controls uniquely “human” things like long-term goal planning, decision making and problem solving. Other studies suggest shrinkage of the (pre)frontal cortex from a DHA deficient diet.
Several studies have found that DHA improves attention, learning, memory and reduces ADHD symptoms in children.
“A recent systematic review [based on 29 studies totalling 102,944 mother child pairs] of the relationship between seafood consumption during pregnancy and child neurodevelopment concluded there was “moderate and consistent evidence” that consumption of commercially available seafood during pregnancy is associated with favorable offspring neurocognitive development.”(S)
Of course those geniuses of the sea - dolphins, and other cetaceans are getting tons of brain-evolving DHA from a diet that is mostly raw fish.
You might say: OK well, dolphins eat tons of fish, why didn’t they just keep getting smarter and smarter - why aren’t they even smarter than humans? Researchers say that might be simply because Smarter brains packed with more neurons use tons of energy and oxygen … if the dolphins’ brains guzzles up more oxygen, then they can’t dive as long.
Speaking of diving, our quest for DHA-rich seafood might explain why our noses are so weird.
Now there’s this old controversial theory called the “aquatic ape theory” that says that humans evolved from an ancestor that adapted to life near bodies of water. Several aspects of our body seem more adapted for the water. For example we don’t have hair on our bodies which would make it easier to swim and we have a layer of fat under our skins unlike other primates which would help us float in water. Further, it may have something to do with why we started walking upright. Monkeys can walk on two feet but they prefer not to, unless they are wading through water. Now most anthropologists completely reject this aquatic ape theory, but whether we had a semi-aquatic ancestor or not, humans are very good at diving. The human spleen for example is larger than other primates and it acts as a reservoir of oxygen-carrying red blood cells allowing us to hold our breath longer.
The Bajau people near the Phillipines live a “sea nomad” type of lifestyle where they spend hours a day diving for all kinds of DHA-rich seafood like shellfish, shrimp, crab, fish, octopus, sea urchin and squid. Their genetics gift them with an abnormally large spleen which is thought to be why some Bajau can hold their breath for over 10 minutes.
Another interesting aspect of humans is our protruding nose. Unlike monkeys flat noses, human noses are better at preventing water from getting in the nasal cavity when we swim or dive. Most monkeys aren’t good swimmers, but proboscis monkeys are …and they happen to have these big protruding noses.
As of 2019, Japan is #1 in the world for IQ with an IQ of 106 - that’s a full 9 points higher than the United States’s 97. Of course there are tons of factors to IQ (S,S2,S3) but Japan does have a DHA-rich food culture that includes plenty of seaweed and fresh seafood - they eat about twice as much fish as Americans. A traditional Japanese breakfast is white rice, fermented soybeans, miso soup with seaweed, roasted fish and more dry seaweed. Of course you can find all kinds of fish at supermarkets and restaurants, but you can even get sushi, fish riceballs or roasted fish at a convenience store. What’s tricky about getting an idea of which country eats the most DHA is that DHA degrades when you heat it. Lucky for Japan, they eat plenty of raw seafood. A 2022 survey found that the second most common way people ate their fish at home in Japan was raw as sashimi. Japan has more than twice as many sushi restaurants than fast food and pizza shops combined.*
*One source puts the number of sushi restaurants at 45,000 , but if we go with the more conservative figure of 22,000 , we would be at double the 6,390 fast food restaurants and 3,700 pizza places. (Some might consider curry and rice bowl chains to be fast food, but even if you include the 4,684 curry shops, and 4,538 rice bowl chains, then we can say there are more sushi shops than all those put together.) Further, there are also 14,000 ‘fish’ restaurants and 50,000 ‘Japanese cuisine’ restaurants. Very often Japanese cuisine includes some fish or at least seaweed.
Now, there’s a 3rd fat that Michael Crawford said was important to brain size that explains why animals like rhinos are so dumb.
Keep reading with a 7-day free trial
Subscribe to Joseph Everett’s WIL Newsletter to keep reading this post and get 7 days of free access to the full post archives.